Are you tired of the slow performance of your laptop’s old processor? Swapping it with a new one can dramatically boost in speed. For instance, upgrading from 2.13GHz Pentium to 2.40GHz Intel Core i5 can raise CPU Benchmarks from 1349 to 2368, but this upgrade isn’t for the fainthearted because it requires advanced skills.
Top Rated Budget Laptops
Last update on 2025-03-30 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
Doesn’t matter that you want to install, replace, or upgrade your laptop processor; this guide will get you covered.
Before removing a single screw, make sure the processor that you’re going to replace is compatible with your Notebook. Even some laptops don’t support the processor upgrade as it is directly soldered on the motherboard.
To understand this process, I have taken the Lenovo G560 laptop; it’s an Intel P6100 model with 2GB memory, 250GB HDD and Intel HD graphics.
How to find a compatible replacement for your old laptop processor upgrades?
1. The simplest way to do it, you can Google “[your notebook model] CPU” – It tells you which CPUs have been sold with your laptop during its lifespan.
2. It’s not the whole story; you should also take a look at the laptop’s service manual. In the specification section, there would be all processors listed the computer was available with.
For Instance: I have downloaded the Lenovo G560 service manual, and what I found it was available with the P6200, i3-380M, and i5-430M processors.
3. You should also visit the official forum of the manufacturer to know which processor has worked for other users with your laptop model.
For instance: On the Lenovo forum, one user has confirmed that the “Intel i3-380M” processor worked well.
Usually, if you have a slim and compact laptop, there are higher chances it has a soldered CPU, and you won’t be able to upgrade. Even some notebook comes with soldered memory (RAM).
If you’re sure that the processor you choose is listed in the service manual and some users have already tested with your laptop model, then you can go further.
So, let’s get ready with the tools to upgrade your laptop processor.
Steps to upgrade a laptop processor in 2024
Step 1: Update the BIOS
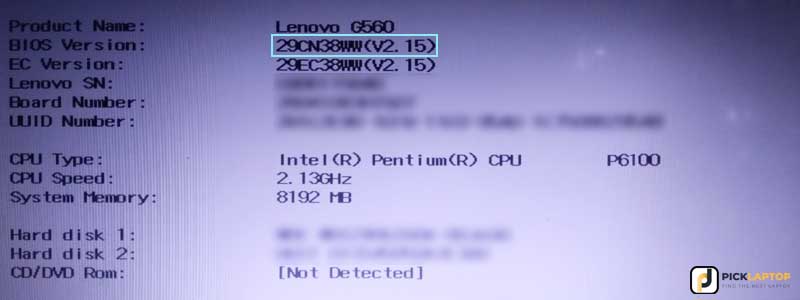
It’s the most critical step before even taking a peek out into the laptop’s internals. You have to make sure your system has the most recent BIOS version; sometimes, manufacturers release these updates to support the newer CPUs.
The gravity behind this matter because if you install the latest chip that your BIOS allows, your system won’t even boot at all. You can check out the latest BIOS version of your laptop by visiting the support section of your manufacturer’s website.
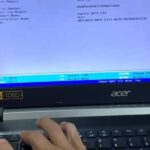
For Instance: The most recent BIOS version of Lenovo G560 is 29CN38WW, according to the manufacturer’s website, and we have updated it as well (see picture).
I am assuming that you have updated your laptop’s bios to the latest, and you’re ready to open your notebook. Wait, did you wear the antistatic wrist strap to protect the internal hardware. Trust me; you don’t want to regret doing all thing “right.”
Got everything; let’s go to the next step.
Step 2: Remove the Battery

All laptops have different designs, but most of the steps are identical when opening any notebook. As I have taken the Lenovo G560 laptop for demonstration, which has a single back cover to access the memory module, hard drive along with processor.
As you have already downloaded the service manual, and it has all the steps, so it won’t be a problem if you have a different laptop.
Removing the battery and dummy card is the first thing to do. However, your laptop might have an inbuilt battery; in this case, you can remove it later.
Note: Laptops will inbuilt battery needs higher caution while opening because the current is still available in a portion of the motherboard. Falling a single screw on the circuit can lead to severe damage.
Step 3: Remove the Back Cover

As you have already disconnected the internal and external power sources, now it’s time to play with screwdrivers and remove the back cover.
In my case, I can access the processor now, as you can see. If you have a different model, I am going to tell you some common steps to disassemble your notebook.
Despite removing the back panels, you’re not able to see the processor; it means you have to take apart the upper part as well. Before going to the next step, now you have to remove all screws presented on the backside.
Note: In some laptop models, screws might be hidden under the rubber part, so make sure to remove them before heading to the next step. Moreover, if the hard disk drive or any component is coming out of the place, you should take it out as well.
Step 4: Remove the Keyboard

As you have already taken apart all screws, it must have loosened the keyboard, DVD writer, and wireless adapter. Now take out the keyboard gently while removing its ribbon cable carefully.
Removing the keyboard might be tricky for some laptops, so don’t rush; an unexpected jerk or excessive force can do unrepairable damage.
If your system has a DVD writer, take it out; also, don’t forget to remove the wireless adapter.
Note: Remember the screw’s place where are they coming from; it comes in handy while assembling.
Step 5: Remove the Upper Shell
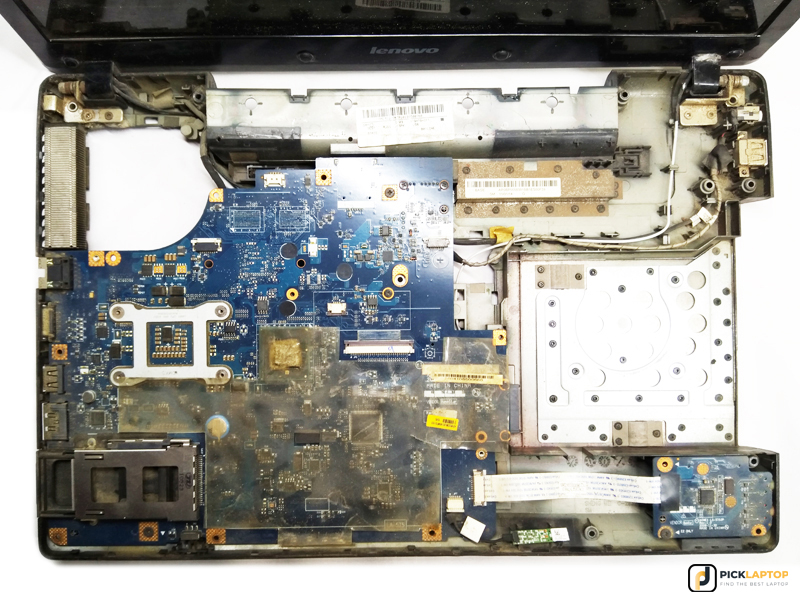
After removing the keyboard, there might be some screws beneath it, remove them. Moreover, if you can see some ribbons and connectors, you should remove them as well.
While removing the upper shell, you have to be careful because there might be any ribbon cable or connector present.
Note: Don’t apply excessive force; if you’re having a problem with removing the upper shell, recheck the bottom area for any hidden screw or part which might be holding it.
Step 6: Remove the Display Assembly
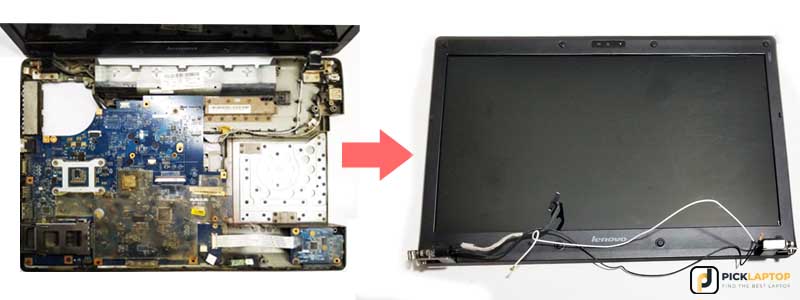
If you already can see the base of the display hinges before removing the upper shell, this step would be performed before step 5; it differs according to the laptops.
Well, unscrew the hinges, unplug the video and Wi-Fi antenna cables, and put the whole display assembly aside.
Step 7: Remove the Heatsink
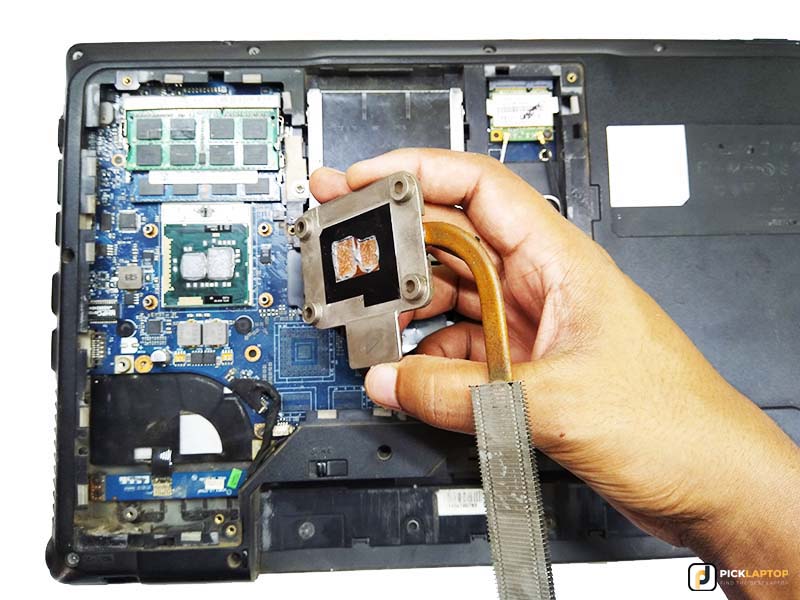

Now you can see the whole motherboard clearly; if your processor is given on the upper side, then you can directly remove the heatsink’s screws and access the processor and graphics card (if available).
If you can’t see the processor yet, you have to take apart the motherboard out of the body.
Note: Please wear the antistatic wrist strap and make it well-grounded before touching any internal parts.
Step 8: Replace the CPU

After putting the heatsink aside, the processor slot should be in front of you. Now turn the CPU socket’s screw anticlockwise until it stops, and lift the processor gently straight up, remove it from the socket, and put it aside. Place the new CPU, and it should be slipped automatically into the slot if appropriately placed. If it looks as it needs a push, there might be a problem with alignment, recheck it.
After successfully placing the CPU don’t forget to lock the CPU socket by turning the screw clockwise.
Note: Some old laptops might have a locking bar instead of a screw on the CPU socket.
Step 9: Apply Thermal Paste and Reassemble
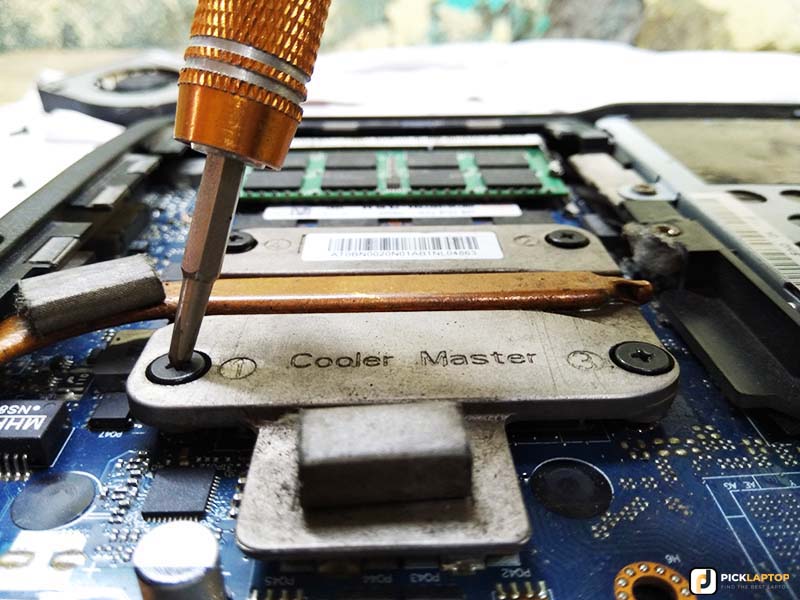


You have to prepare the heatsink anew – remove all old thermal paste (silver-gray gunk) with 99% isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free rag, if you have purchased an old CPU then make it clean as well.
After drying out, apply a thin layer of thermal paste to the top of the CPU, and spread it evenly with a plastic card. Put the heat sink and reassemble the laptop.
After booting up, enter the BIOS and check the laptop can see the CPU correctly.
Finally, launch Windows and enjoy the higher performance of your new processor.
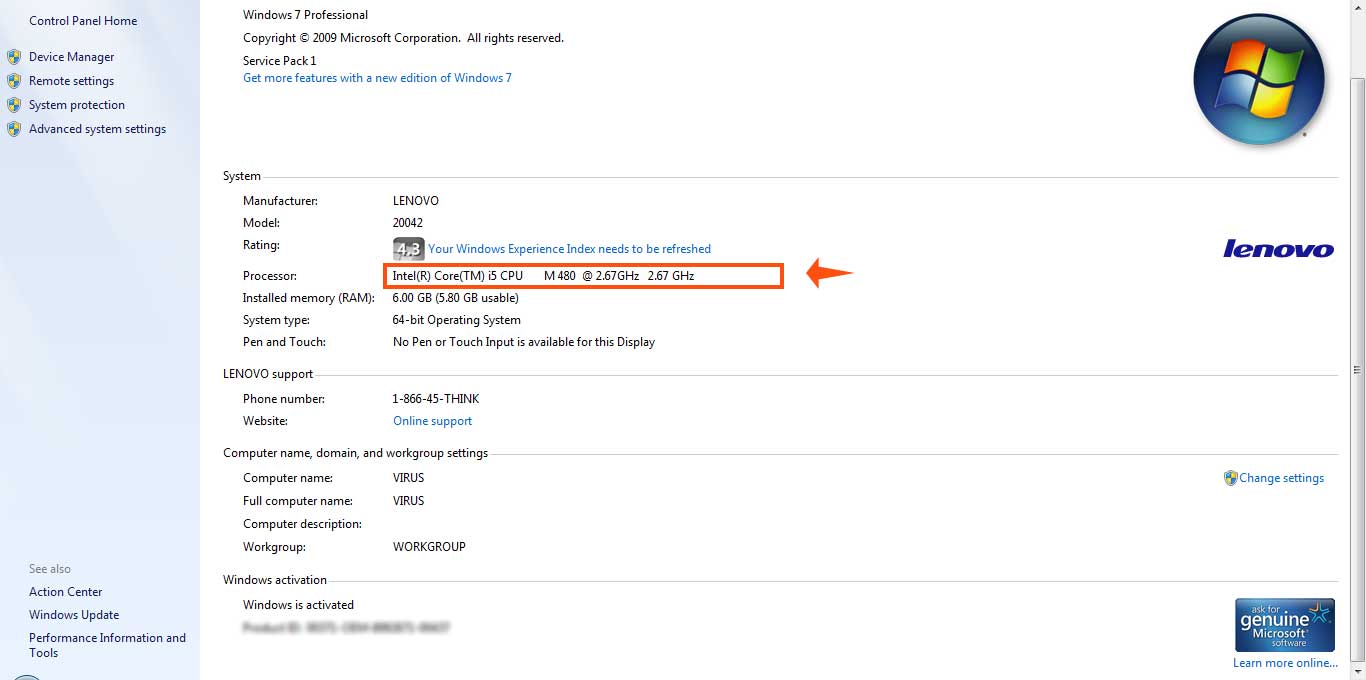
Note: Sometimes, Windows might fail to boot after placing a new processor, and you might need to reinstall it.






This website truly has all of the information I needed about
this subject and didn’t know who to ask.